Chemical Tests for the Presence of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
This is part of the HSC Chemistry course under the section: Analysis of Organic Substances.
HSC Chemistry Syllabus
- Conduct qualitative investigations to test for the presence in organic molecules of the following functional groups:
Chemical Tests For Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
This video explores how qualitative chemical tests such as oxidation can distinguish between an aldehyde and ketone. The video also explores qualitative tests for the presence of carboxylic acids.
Chemical Tests For Aldehydes and Ketones
|
Acidified dichromate (Cr2O72–/H+) Oxidation Test
$$\frac{1}{2}Cr_2O_7^{2-} + 7H^+ + 3e^- \rightleftharpoons Cr^{3+} + \frac{7}{2}H_2O$$
|
Observation for different types of alcohol
|
|
Acidified Permanganate (MnO4–/H+) Oxidation Test
$$MnO_4^- + 8H^+ + 5e^- \rightleftharpoons Mn^{2+} + 4H_2O$$
|
|
Chemical Tests For Carboxylic Acids
Using pH Indicators
- A solution containing carboxylic acid will have a pH < 7 at 25ºC. This means a blue litmus paper will turn red, bromothymol blue will be yellow.
- Ketones and aldehydes do not contain acidic hydrogens so their solutions will be neutral.

Sodium Carbonate Test
Carboxylic acids undergo acid-base reaction with carbonate and hydrogen carbonates to produce salt, water and carbon dioxide. No acid and base reactions occur between an aldehyde/ketone and carbonates.
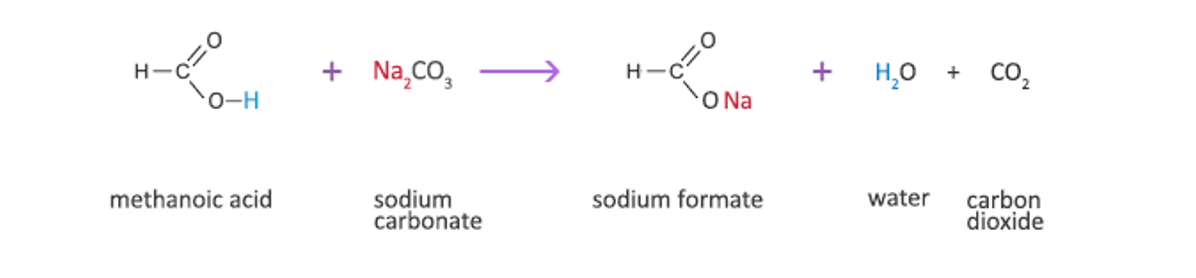

When Na2CO3 or NaHCO3 is added to a test tube, formation of bubbles indicates the production of carbon dioxide, which in turn indicates the presence of a carboxylic acids.
Production of CO2 can be further confirmed by using limewater test by adding calcium hydroxide (lime water). The presence of carbon dioxide would react with lime water to produce calcium carbonate, causing the solution to turn cloudy and milky.
CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)

Limewater test of carbon dioxide: solution of calcium hydroxide (left) and calcium carbonate formation after carbon dioxide is bubbled into the solution (right).
RETURN TO MODULE 8: APPLYING CHEMICAL IDEAS
 Cr6+ (orange) reduces to form Cr3+(green)
Cr6+ (orange) reduces to form Cr3+(green)
 Mn7+ (purple) reduces to form Mn2+ (colourless)
Mn7+ (purple) reduces to form Mn2+ (colourless)