Isomers
This is part of HSC Chemistry course under the topic of Hydrocarbons.
HSC Chemistry Syllabus
- explore and distinguish the different types of structural isomers, including saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, including: (ACSCH035)
What are Isomers?
Isomers are compounds which share the same molecular formula but different structure. There are three types of isomers to be explored in HSC Chemistry:
- chain isomers
- position isomers
- functional group isomers
Chain Isomers
Chain isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of its carbon chain (stem).
For example, pentane and 2-methyl butane are both alkanes with five carbon atoms and therefore the same molecular formula C5H12. Yet, they are different structural formulae.
|
Pentane (C5H12) |
Methylbutane (C5H12) |
Position Isomers
Position isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula and functional group, but the position of the functional group is different.
For example, 1-butene and 2-butene both have the same molecular formula C4H8 but the position of the double bond is in different positions.
|
1-butene (C4H8) |
2-butene (C4H8) |
Functional Group Isomers
Functional group isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different functional groups.
There are three common pairs of functional groups which can exhibit isomerism:
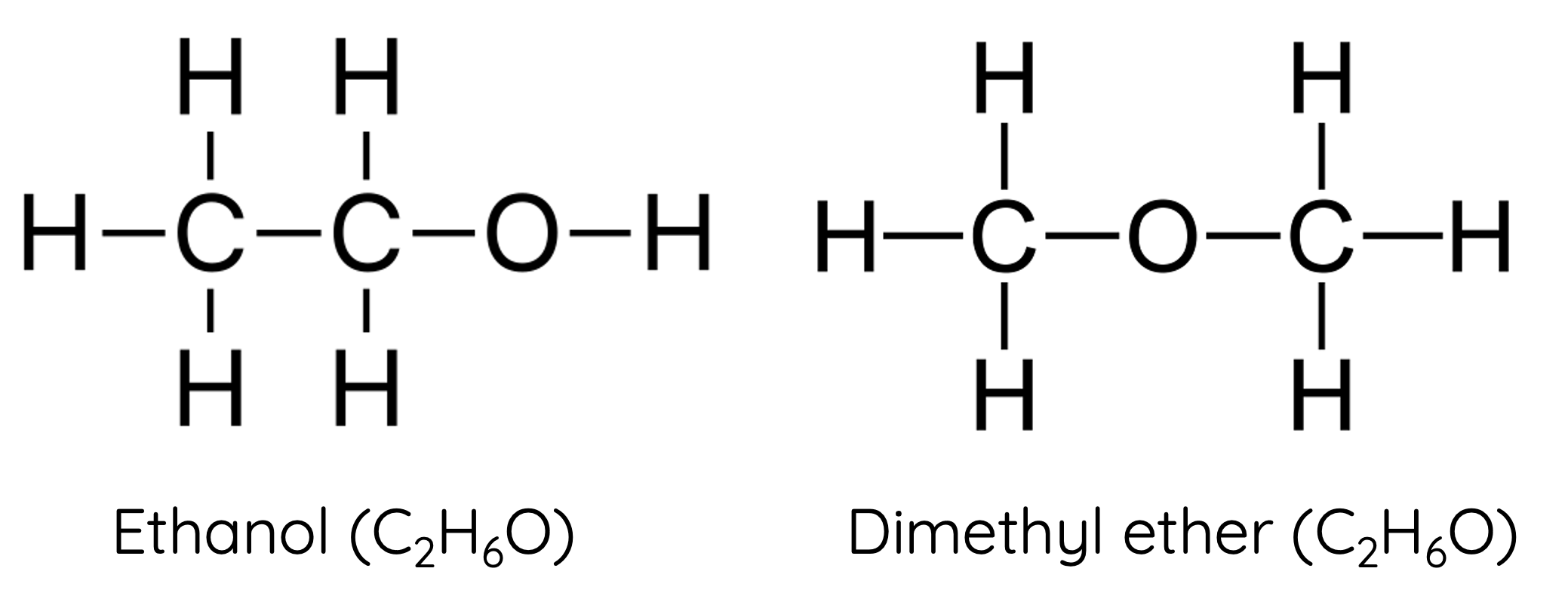
Ethers and Alcohols
Ethers (not included in HSC Chemistry syllabus) and alcohols can be functional group isomers.
For example, ethanol and dimethyl ether are functional group isomers:
Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones can be functional group isomers. It is important to note that these two functional groups are not position isomers.
For example, propanal and propanone are functional group isomers:

Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Carboxylic acids and esters can be functional group isomers as their molecular formulae are identical when the number of carbon atoms are equal.
For example, propanoic acid has two functional group isomers: ethyl methanoate and methyl ethanoate.




